

Adler from the wealthy Danish Jewish Adler banking family.

Niels Henrik David Bohr was born in Copenhagen, Denmark, on 7 October 1885, the second of three children of Christian Bohr, a professor of physiology at the University of Copenhagen, and Ellen Bohr (née Adler), who was the daughter of David B. He was involved with the establishment of CERN and the Research Establishment Risø of the Danish Atomic Energy Commission and became the first chairman of the Nordic Institute for Theoretical Physics in 1957. After the war, Bohr called for international cooperation on nuclear energy. From there, he was flown to Britain, where he joined the British Tube Alloys nuclear weapons project, and was part of the British mission to the Manhattan Project. In September 1943 word reached Bohr that he was about to be arrested by the Germans, and he fled to Sweden. After Denmark was occupied by the Germans, he had a famous meeting with Heisenberg, who had become the head of the German nuclear weapon project. Later, the element bohrium was named after him.ĭuring the 1930s, Bohr helped refugees from Nazism. He predicted the existence of a new zirconium-like element, which was named hafnium, after the Latin name for Copenhagen, where it was discovered.

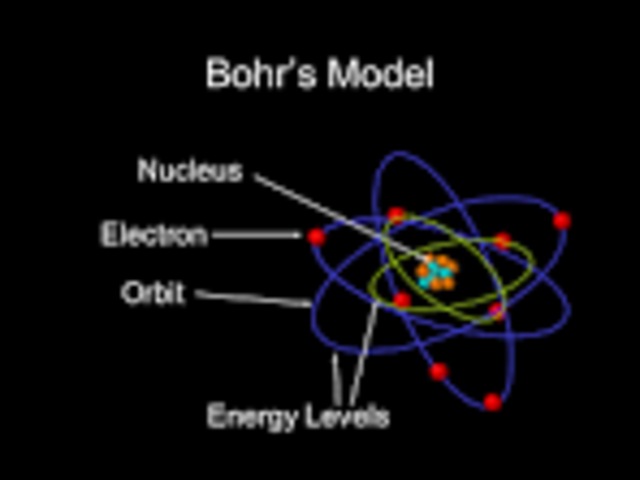
Bohr mentored and collaborated with physicists including Hans Kramers, Oskar Klein, George de Hevesy, and Werner Heisenberg. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy.īohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen, now known as the Niels Bohr Institute, which opened in 1920. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research.īohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. In 1957, Bohr received the Atoms for Peace Award for his trailblazing theories and efforts to use atomic energy responsibly.Niels Henrik David Bohr ( Danish: 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. He helped to establish CERN, a Europe-based particle physics research facility, in 1954 and put together the Atoms for Peace Conference of 1955. In his "Open Letter to the United Nations," dated June 9, 1950, Bohr envisioned an "open world" mode of existence between countries that abandoned isolationism for true cultural exchange. Atoms for PeaceĪfter the end of the war, Bohr returned to Europe and continued to call for peaceful applications of atomic energy. Because he had concerns about how the bomb could be used, he called for future international arms control and active communication about the weapon between nations - an idea met with resistance by Winston Churchill and Franklin D. Bohr then worked with the Manhattan Project in Los Alamos, New Mexico, where the first atomic bomb was being created.
Once Denmark became occupied by Nazi forces, the Bohr family escaped to Sweden, with Bohr and his son Aage eventually making their way to the United States. With Adolf Hitler's rise in power, Bohr was able to offer German Jewish physicists refuge at his institute in Copenhagen, which in turn led to travel to the United States for many.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
